As Omicron Surges, Effort to Vaccinate Young Children Stalls

Two months after Pfizer’s covid-19 vaccine was authorized for children ages 5 to 11, just 27% have received at least one shot, according to Jan. 12 data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Only 18%, or 5 million kids, have both doses. (Scroll down for Eastern Shore statistics.)
The national effort to vaccinate children has stalled even as the omicron variant upends schooling for millions of children and their families amid staffing shortages, shutdowns, and heated battles over how to safely operate. Vaccination rates vary substantially across the country, a Kaiser Health News analysis of the federal data shows. Nearly half of Vermont’s 5- to 11-year-olds are fully vaccinated, while fewer than 10% have gotten both shots in nine other, mostly Southern, states.
Pediatricians say the slow pace and geographic disparities are alarming, especially against the backdrop of record numbers of cases and pediatric hospitalizations. School-based vaccine mandates for students, which some pediatricians say are needed to boost rates substantially, remain virtually nonexistent.
“You have these large swaths of vulnerable children who are going to school,” said Dr. Samir Shah, a director at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Compounding the problem is that states with low vaccination rates “are less likely to require masking or distancing or other nonpartisan public health precautions,” he said.
In Louisiana, where 5% of kids ages 5 to 11 have been fully vaccinated, Gov. John Bel Edwards, a Democrat, added the shot to the list of required school immunizations for the fall, over the objections of state legislators, who are mostly Republicans. The District of Columbia and California, where about 1 in 5 elementary school kids are fully vaccinated, have added similar requirements. But those places are the exceptions — 15 states have banned covid vaccine mandates in K-12 schools, according to the National Academy for State Health Policy.
Mandates are one of multiple “scientifically valid public health strategies,” Shah said. “I do think that what would be ideal; I don’t think that we as a society have a will to do that.”
Vaccine demand surged in November, with an initial wave of enthusiasm after the shot was approved for younger children. But parents have vaccinated younger kids at a slower pace than 12- to 15-year-olds, who became eligible in May. It took nearly six weeks for 1 in 5 younger kids to get their first shot, while adolescents reached that milestone in two weeks.
Experts cite several factors slowing the effort: Because kids are less likely than adults to be hospitalized or die from the virus, some parents are less inclined to vaccinate their children. Misinformation campaigns have fueled concerns about immediate and long-term health risks of the vaccine. And finding appointments at pharmacies or with pediatricians has been difficult.
“One of the problems we’ve had is this perception that kids aren’t at risk for serious illness from this virus,” said Dr. Yvonne Maldonado, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Diseases. “That’s obviously not true.”
Parents are left to weigh which is more of a threat to their children: the covid virus or the vaccine to prevent the virus. Overwhelmingly, research shows, the virus itself presents a greater danger.
Kids can develop debilitating long-covid symptoms or a potentially fatal post-covid inflammatory condition. And new research from the CDC found that children are at significantly higher risk of developing diabetes in the months after a covid infection. Other respiratory infections, like the flu, don’t carry similar risks.
Katharine Lehmann said she had concerns about myocarditis — a rare but serious side effect that causes inflammation of the heart muscle and is more likely to occur in boys than girls — and considered not vaccinating her two sons because of that risk. But after reading up on the side effects, she realized the condition is more likely to occur from the virus than the vaccine. “I felt safe giving it to my kids,” said Lehmann, a physical therapist in Missouri, where 20% of younger kids have gotten at least one dose.
Recent data from scientific advisers to the CDC found that myocarditis was extremely rare among vaccinated 5- to 11-year-olds, identifying 12 reported cases as of Dec. 19 out of 8.7 million administered doses.
The huge variations in where children are getting vaccinated reflect what has occurred with other age groups: Children have been much less likely to get shots in the Deep South, where hesitancy, political views, and misinformation have blunted adult vaccination rates as well. Alabama has the lowest vaccination rate for 5- to 11-year-olds, with 5% fully vaccinated. States with high adult vaccine rates such as Vermont, Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Maine have inoculated the greatest shares of their children.
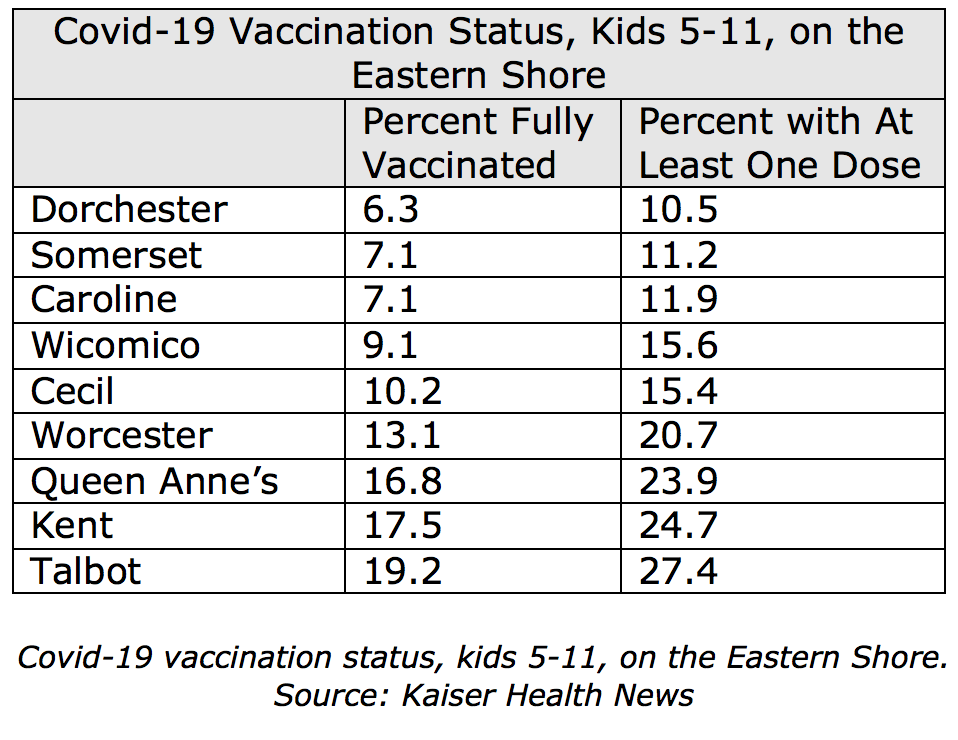
Even within states, rates vary dramatically by county based on political leanings, density, and access to the shot. More than a quarter of kids in Illinois’ populous counties around Chicago and Urbana are fully vaccinated, with rates as high as 38% in DuPage County. But rates are still below 10% in many of the state’s rural and Republican-leaning counties. In Maryland, where 1 in 4 kids are fully vaccinated, rates range from more than 40% in Howard and Montgomery counties, wealthy suburban counties, to fewer than 10% along parts of the more rural Eastern Shore.
Nationally, a November Kaiser Family Foundation poll found that 29% of parents of 5- to 11-year-olds definitely won’t vaccinate their children and that an additional 7% would do so only if required. Though rates were similar for Black, White and Hispanic parents, political differences and location divided families. Only 22% of urban parents wouldn’t vaccinate their kids, while 49% of rural parents were opposed. Half of Republican parents said they definitely wouldn’t vaccinate their kids, compared with just 7% of Democrats.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Common Sense for the Eastern Shore







