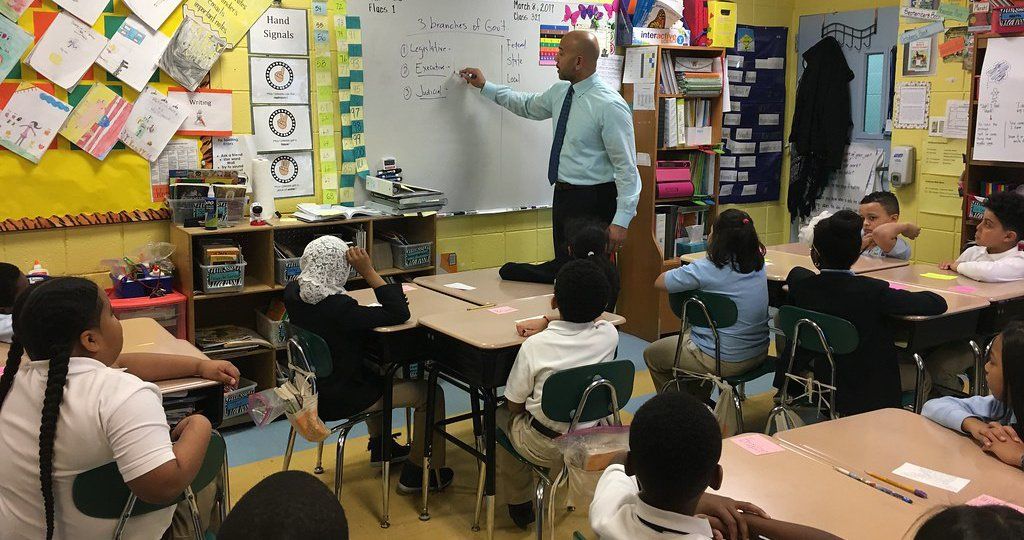
After Capitol Riot, Some States Turn to Civics Education
Matt Vasilogambros, Pew Charitable Trusts • June 22, 2021
After waiting two hours for her chance to speak, high school student Samantha Oliver spoke up at the Delaware House Education Committee’s hearing recently with a succinct message: Young people should be active participants in our democracy.
“It is a necessity that we, the next generation, learn how to use our voices for good, for change, effectively and earnestly,” said Oliver, a junior at the Sussex Academy of Arts, on the Zoom call. “We will be the ones to lead the charge of our country for the years to come.”
She was speaking in favor of a measure that would give sixth- through 12th-grade students one excused absence per year from school to participate in a civic activity such as attending a rally or visiting the state capitol. If the bill passes, Delaware will become the only state to offer this opportunity to students.
The deadly insurrection at the U.S. Capitol in January and the continuing misinformation about the presidential election have left many Americans deeply worried about the state of their democracy. Some legislators on both sides of the aisle say the extreme political divisions spring in part from a fundamental lack of understanding about the country’s history and how its government works.
It’s a fragile time in our democracy, said Shawn Healy, senior director of state policy and advocacy at iCivics, a Massachusetts-based education nonprofit that released a roadmap earlier this year outlining how states, local school districts, and educators can reinvigorate civics and history education around the country.
As the U.S. has disinvested in civics education, school boards have poured money into science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) coursework. The U.S., in fact, spends a thousand times more per student on STEM education than on history and civics, according to the Center for Civic Literacy at Indiana University.
The lack of investment shows: A quarter of Americans cannot name a single branch of government, according to a 2020 national survey by the Annenberg Public Policy Center at the University of Pennsylvania.
Many young people are dissatisfied with the limited civics coursework they receive.
Nationwide, lawmakers are considering a variety of measures. In New Jersey, the state Senate passed a measure that would require civics coursework in middle school. Meanwhile, both houses of the Florida legislature passed a bill that would offer school districts a civics literacy project.
The YMCA has been involved in nonpartisan civics education since 1936. Over 55,000 students in 42 states and the District of Columbia participate in its model government program, Youth and Government. Many of those students have implored their states to pass legislation that bolsters civics education.
Some states are also moving to require students to pass the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Service civics test required for naturalization. The 128 questions range from the number of U.S. Supreme Court justices to why the United States entered World War II. Around half of states have similar requirements.
Most Democrats oppose these measures, worried the test is not an effective tool for bolstering civic knowledge. Using the naturalization test as a benchmark for civics education is flawed and shortsighted, said Khalilah Harris, acting vice president of K-12 education at the Center for American Progress, a Washington, D.C.-based progressive think tank. The organization has released two reports in recent years that outline the gaps in U.S. civics education.
Students of different backgrounds and economic levels have uneven educational experiences, she said, and the test could disproportionately hurt low-income communities or communities of color by risking students’ graduation.
“Adding another required graduation assessment does not address the needs of the district to have adequate resources, funding, or exposure to things like a trip to the Liberty Bell,” Harris said.
Harris said other measures would more effectively involve students in civic life: States could allow 16-year-olds to vote in local municipal elections. School boards could give students full voting rights on issues that affect them. States also could implement automatic voter registration, which would add young people to voter rolls when they get their driver’s license.
Some conservatives worry investments in civics education will open the door to teaching critical race theory, an academic field that examines racism in systems.
Several Republican-controlled states, including Idaho, Iowa, and Tennessee, have enacted measures this session that would ban materials that discuss the racist roots of America’s founding, including the New York Times’ “1619 Project.”
On the federal level, a bipartisan bill would invest $1 billion a year for six years in civics and history education, with money given to states for education programs, to nonprofits for civics programs for underserved communities, and to higher education programs for training educators. It would be up to school districts and schools to craft the curricula.
Some Republicans argue that civics education could lead to un-American indoctrination. Healy, of iCivics, said this argument is a dangerous distraction, meant to stir up the culture war debate. And some legislators worry that teenagers aren't mature enough to benefit from more opportunities to engage with the government.
After the public comment concluded for the Delaware bill that would give students an excused absence for a civic-related activity, Republican state Rep. Richard Collins criticized the bill.
“Our kids, they go to school to learn,” he said, exasperated. “It really does bother me. They need to learn before they become activists, so they have informed opinions. I’m sorry, I just cannot support this bill.”
As he finished, the committee chair, Democratic state Rep. Kimberly Williams, cut in.
“Learning comes in all different ways,” she said. “It’s not just sitting behind a desk.”
Matt Vasilogambros writes about immigration and voting rights for Stateline. Before joining Pew, he was a writer and editor at The Atlantic, where he covered national politics and demographics. Previously, he was a staff correspondent at National Journal and has written for Outside. In 2017, he completed the 2,650-mile Pacific Crest Trail. He is a graduate of Drake University.
The Pew Charitable Trusts is a global research and public policy change agent that remains nonpartisan and dedicated to serving the public. An independent non-profit organization, the Pew Trusts seeks to improve public policy, inform the public, and invigorate civic life.
Common Sense for the Eastern Shore

When I practiced law, much of my litigation involved issues arising under federal antitrust laws. The Department of Justice (DOJ) was my frequent adversary in court. In some cases, DOJ challenged a client’s conduct as anticompetitive. In others, they claimed an intended client merger would create a monopoly. Some of these DOJ court battles were won, others were not. Overall, I had great respect for DOJ lawyers. They were professional, well prepared, and dedicated to their mission of seeing justice done. They were courteous, honest, and forthright with the courts before which we argued our cases. In those days, without resorting to social media or press conferences, the DOJ spoke entirely through its court filings. Although as an advocate I took issue with various DOJ investigatory decisions as well as decisions to initiate litigation, I never thought politics was involved. Post-Watergate internal rules strictly limited communication with any figures at the White House. Not so, it seems, anymore. Beginning last January 20, all of this changed rapidly and spectacularly . On March 14, Trump triumphantly arrived at the main DOJ building in D.C. to be welcomed by a group of carefully selected VIPs. He was greeted by Pam Bondi, his chosen new attorney general, who exclaimed, “We are so proud to work at the directive (sic) of Donald Trump.” Bondi’s boast that the DOJ now worked at the president’s behest was something never said before and, in effect, surrendered the department’s long and proud independence. And Bondi’s comment was not an empty gesture. As chronicled by reporters Carol Leonnig and Aaron Davis in their new book, Injustice: How Politics and Fear Vanquished America’s Justice Department , within hours of being sworn in, Trump and his lieutenants began punishing those at the Justice Department who had investigated him or those he considered his political enemies. Career attorneys with years of experience under many administrations were fired or reassigned to lesser work, or they resigned. As Leonnig and Davis report, what followed was “the wholesale overthrow of the Justice Department as Trump insert[ed] his dutiful former defense attorneys and 2020 election deniers atop the department.” [Source: Injustice , p. xix.] In the place of years of experience, the new team appears credentialed simply by loyalty to the president’s causes. The DOJ’s conduct in court has since caused damage to judicial and public faith in the integrity and competence of the department. Just Security is an independent, non-partisan, daily digital law and policy journal housed in the Reiss Center on Law and Security at the New York University School of Law. Since January 20, it has documented federal judicial concerns about DOJ conduct. In 26 cases, judges raised questions about DOJ non-compliance with judicial orders and in more than 60 cases, judges expressed distrust of government-provided information and representations. This count was taken the day after a federal court dismissed the DOJ cases against former FBI Director James Comey and New York Attorney General Letitia James. [Source: Just Security , “The ‘Presumption of Regularity’ in Trump Administration Litigation,” Nov. 20, 2025.] As summarized by the Georgetown Law Center’s Steve Vladeck, “It’s one thing for the Department of Justice to so transparently pursue a politically motivated prosecution. But this one has been beset from the get-go with errors that remotely competent law students wouldn’t make. Indeed, it seems a virtual certainty that the Keystone Kops-like behavior of the relevant government lawyers can be traced directly to the political pressure to bring this case; there’s a reason why no prosecutors with more experience, competence, or integrity were willing to take it on.” [Source: One First , Nov. 24, 2025.] Rather than accept criticism and instead of trying to do better, Bondi’s DOJ and the Trump administration lash out in a fashion apparently aimed at demeaning the federal judiciary. At a recent Federalist Society’s National Lawyers Convention, Deputy Attorney General Todd Blanche, one of Trump’s former defense attorneys, attributed the Trump administration’s myriad losses in the lower federal courts to “rogue activist judges.” He added, “There’s a group of judges that are repeat players, and that’s obviously not by happenstance, that’s intentional, and it’s a war, man.” Deputy Chief of Staff Stephen Miller decries each adverse ruling against the Trump administration as just part of a broader “judicial insurrection.” Not to be left behind, Trump himself regularly complains of “radical left lunatic” judges. In addition to the harm these comments inflict on the federal courts, their premise is simply not true. According to a survey by Vladeck, as of Nov. 14, there were 204 cases in which federal district courts have ruled on requests for preliminary relief against the Trump administration. In 154 of them, district judges granted either a temporary restraining order, a preliminary injunction, or both. Those 154 rulings came from 121 district judges appointed by seven presidents (including President Trump) in 29 district courts. In the 154 cases with rulings adverse to the Trump administration, 41 were presided over by 30 Republican-appointed judges, fully half of whom were appointed by President Trump. No, it is no longer your grandfather’s Department of Justice. John Christie was for many years a senior partner in a large Washington, D.C. law firm. He specialized in anti-trust litigation and developed a keen interest in the U.S. Supreme Court about which he lectures and writes.
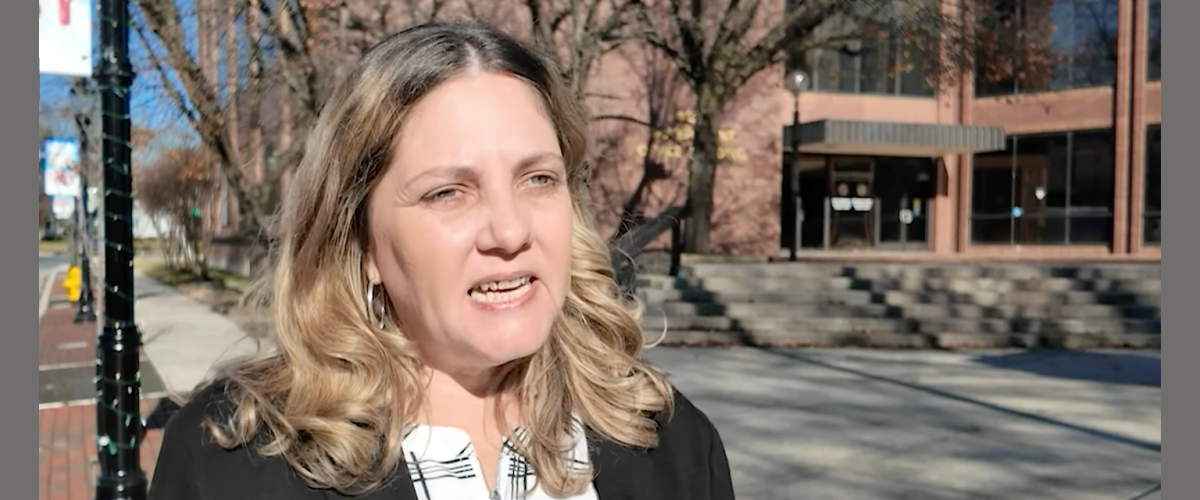

The Salisbury City Council has appointed longtime public servant Melissa D. Holland to fill the vacancy in District 2. Holland was selected on Dec. 1 after the council reviewed several applicants. A 27-year resident of Salisbury, Holland brings more than 20 years of experience in government, education, and administration. As executive assistant to the president of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science, she currently oversees operations, budgeting, communications, and planning. Before joining UMCES, Holland worked for nearly 11 years with the Wicomico County Council, gaining extensive experience in legislative procedure, constituent services, research, and budget preparation. Her background includes positions with the Wicomico County Board of Education, the State of Maryland’s Holly Center, and multiple early-learning programs. Approved by a 3-1 council vote, Holland was selected based on her administrative expertise and long-standing community involvement. (Salisbury’s City Council is now comprised of only women.) She has a bachelor’s degree in legal studies from Post University and an associate degree from Wor-Wic Community College. She has also served as PTA president at East Salisbury Elementary and Wicomico Middle School. In her application, Holland emphasized her commitment to maintaining transparency in city government and ensuring that District 2 residents remain informed and represented. “I plan to be well-informed on the issues that matter to the citizens of Salisbury and to listen to their concerns carefully,” she wrote. “I want to make a positive and lasting impact on our city.” Holland’s appointment restores the City Council to full membership as it faces debates over budgeting, infrastructure planning, and local governance initiatives. She is expected to begin constituent outreach immediately and participate fully in the selection of the next council president.

Voters in Hurlock have delivered sweeping changes in this year’s municipal election, as Republican and GOP-aligned candidates won key races there. The results mark a setback for Democrats and a significant political shift in a community that has historically leaned Democratic in state and federal contests. The outcome underscores how local organizing and turnout strategies can have an outsized impact in small-town elections. Analysts also suggest that long-term party engagement in municipal contests could shape voter alignment in future county and state races. Political analysts warn that ignoring municipal elections and ceding them to the GOP could hurt the Maryland Democratic Party in statewide politics. Turnout increased by approximately 17% compared with the 2021 municipal election, reflecting heightened local interest in the mayoral and council races. Incumbent Mayor Charles Cephas, a Democrat, was soundly defeated by At-Large Councilmember Earl Murphy, who won with roughly 230 votes to Cephas’s 144. In the At-Large Council race, Jeff Smith, an independent candidate backed by local Republicans, secured a 15-point win over Cheyenne Chase. In District 2, Councilmember Bonnie Franz, a Republican, was re-elected by 40 percentage points over challenger Zia Ashraf, who previously served on the Dorchester Democratic Central Committee. The only Democrat to retain a seat on the council was David Higgins, who was unopposed. The Maryland Republican Party invested resources and campaign attention in the Hurlock race, highlighting it on statewide social media and dispatching party officials, including Maryland GOP Chair Nicole Beus Harris, to campaign. Local Democrats emphasized support for Mayor Cephas through the Dorchester County Democratic Central Committee, but the Maryland Democratic Party did not appear to participate directly.
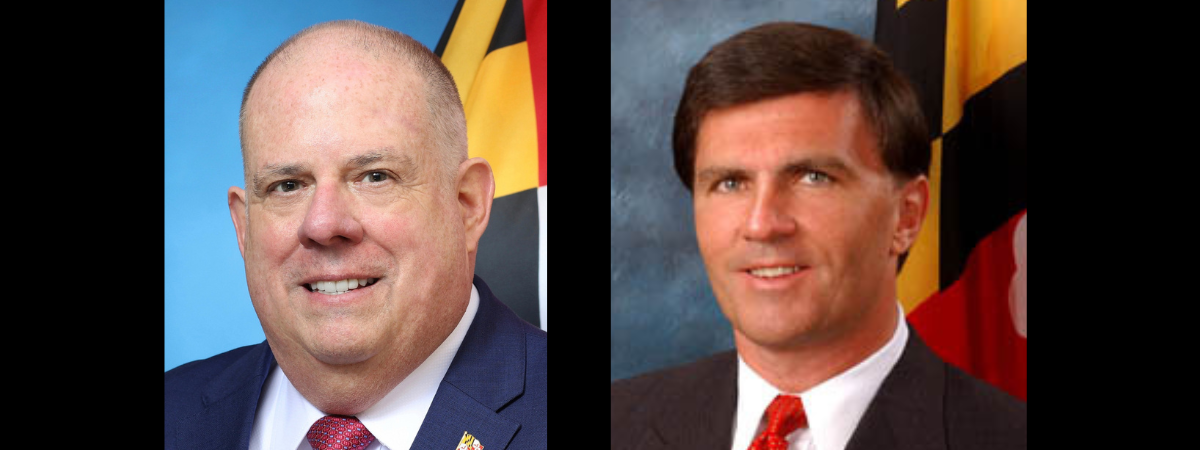

In what political observers are calling a clear break from Maryland’s moderate Republican establishment, Wicomico County Executive Julie Giordano chose former Gov. Bob Ehrlich — not former Gov. Larry Hogan — as the guest of honor at her re-election fundraiser in late October. Billed as Giordano’s annual Harvest Party, her event drew conservative activists from across the lower Eastern Shore and featured Ehrlich as keynote speaker. This was immediately read by insiders as a signal that Giordano will embrace the party’s right-wing base ahead of 2026, distancing herself from Hogan’s more centrist, bipartisan image. “Bringing in Bob Ehrlich instead of Larry Hogan wasn’t accidental,” one longtime Republican strategist said. “It shows Giordano wants to plant her flag with the MAGA-aligned wing of the party, the same voters who now dominate Maryland’s Republican primary base.” Hogan, who has hinted at another run for governor, was notably absent from this year’s Tawes Crab and Clam Bake in Somerset County, a high-profile gathering long considered essential for statewide contenders. Coupled with Giordano’s public alignment with Ehrlich, Hogan’s absence has fueled speculation that his influence within Maryland’s GOP is slipping. Those doubts were amplified by new polling data. A statewide survey commissioned by the Baltimore Banner found Gov. Wes Moore (D) leading Hogan 45% to 37% in a hypothetical 2026 matchup, with 14% undecided. The poll, conducted by phone and web from Oct. 7–10 among more than 900 registered voters, carries a margin of error of 3.2 percentage points. The results suggest that while Hogan remains popular among moderates and independents, Moore continues to hold a firm advantage statewide, particularly among Democrats and younger voters. Giordano’s decision to align herself with Ehrlich rather than Hogan further illustrates the ideological divide defining Maryland Republicans heading into 2026. As the party drifts further to the right, analysts say Hogan’s brand of pragmatic centrism may no longer have a natural home in today’s GOP. For now, Ehrlich’s appearance in Salisbury is being seen as a symbolic moment, one that cements Giordano’s status as a leading figure in the state’s Trump-aligned movement and underscores how quickly the political winds have shifted. For Hogan, once seen as the Republican best positioned to reclaim the governor’s office, that shift may mark the end of an era.

Can Maryland create a new congressional map that will flip the state’s sole Republican district to the Democrats? Gov. Wes Moore has created a Governor's Redistricting Advisory Commission to consider mid-cycle redistricting and Maryland has jumped into the redistricting fray. The commission will conduct public hearings, solicit public feedback, and present recommendations to the governor and Maryland General Assembly. “My commitment has been clear from day one — we will explore every avenue possible to make sure Maryland has fair and representative maps,” said Moore. “And we also need to make sure that, if the president of the United States is putting his finger on the scale to try to manipulate elections because he knows that his policies cannot win in a ballot box, then it behooves each and every one of us to be able to keep all options on the table to ensure that the voters’ voices can actually be heard .” Moore’s commission is one of those options — a response to Trump’s call to Republican-led states to create more GOP House districts before the 2026 midterm elections. Three GOP states — Texas, Missouri, and North Carolina — have completed a Trump gerrymander for a gain of seven seats and three more states — Indiana, Utah, and Ohio — could create new maps with a total of four additional Republican seats. That would make 11, should they withstand challenges. Democratic-led states made a lot of noise at first about countering these GOP efforts, but only California and Virginia have campaigns for new maps underway. California wants to flip five seats and Virginia hopes for up to four. Optimistically, that could add up to as many as nine. Maryland’s goal would be to add one Democratic seat. Other states on both sides could soon follow, in some cases taking advantage of existing redistricting deadlines or ongoing litigation. Maryland State Senate President Bill Ferguson (D-Balto City) is not in favor of mid-cycle redistricting, calling it too dicey. “Simply put, it is too risky and jeopardizes Maryland’s ability to fight against the radical Trump administration. At a time where every seat in Congress matters, the potential for ceding yet another one to Republicans here in Maryland is simply too great,” Ferguson wrote in a letter to Senate Democrats. Rep. Andrew P. Harris (R-MD01), whose district would be targeted by redistricting, called the effort "the most partisan thing you could do." He whined, “It just wouldn’t be fair.” Harris warned that any redistricting could backfire on the Democrats. “We will take this to court, it will go as high as necessary, and in the end, a judge could draw a map that actually has two or three Republican congressmen,” Harris said. “I’d caution the Democrats, be careful what you wish for.” Harris and his wife, Maryland GOP Chair Nicole Beus Harris, have perhaps already worked out a strategy. The Governor’s Redistricting Advisory Commission, last constituted by Gov. Martin O’Malley in 2011, will begin its work this month. The five-member commission includes: Chair: Senator Angela Alsobrooks Senate President Bill Ferguson or designee Speaker Adrienne A. Jones or designee Former Attorney General Brian Frosh Cumberland Mayor Ray Morriss “We have a president that treats our democracy with utter contempt. We have a Republican party that is trying to rig the rules in response to their terrible polling,” said Sen. Alsobrooks. “Let me be clear: Maryland deserves a fair map that represents the will of the people. That’s why I’m proud to chair this commission. Our democracy depends on all of us standing up in this moment.” Will Maryland’s First District finally be competitive? Can we at long last replace “AWOL Andy” Harris? Stay tuned…. Jan Plotczyk spent 25 years as a survey and education statistician with the federal government, at the Census Bureau and the National Center for Education Statistics. She retired to Rock Hall.

In strong numbers, local residents turned out last month for a community information session on offshore wind hosted by the Alliance for Offshore Wind at the Ocean Pines library. The forum heard from industry experts, environmental advocates, and labor leaders to discuss how offshore wind projects can support jobs, clean energy, and coastal resilience along Maryland’s Eastern Shore. Featured were Sam Saluto of Oceantic, Jim Strong of the United Steelworkers, Ron Larsen of Sea Ink Solutions, and Jim Brown of the Audubon Society, all of whom emphasized the long-term environmental and economic benefits of wind development off Maryland’s coast. Speakers outlined how the project, once completed, is expected to create hundreds of high-paying jobs, generate clean power for tens of thousands of homes, and reduce reliance on fossil fuels that cause pollution and coastal erosion. “The potential here is extraordinary,” said Saluto, highlighting Oceantic’s ongoing work to ensure safety and sustainability standards remain at the highest level. “We’re not just talking about wind turbines. We’re talking about revitalizing local economies and protecting the Shore’s way of life.” Union representative Jim Strong echoed that sentiment, noting that Maryland’s labor community sees offshore wind as a chance to rebuild domestic manufacturing capacity while giving workers access to strong wages and long-term stability. Environmental voices, including Jim Brown of the Audubon Society, focused on how properly sited wind projects can reduce carbon emissions while coexisting with marine wildlife and migratory bird patterns. While most of the evening centered on data and community questions, the event briefly turned tense when Ocean City Mayor Rick Meehan, who is leading a lawsuit challenging Maryland’s offshore wind plans, attempted to question the panel. The mayor appeared to lose his train of thought mid-sentence and later cast doubt on the reality of climate change, drawing visible concern from several attendees. Meehan, a New Yorker who moved to Ocean City in 1971 and has held public office since 1985, has become one of the region’s most vocal opponents of offshore wind. His critics argue the lawsuit represents an effort to stall progress rather than engage with the facts presented by energy, labor, and environmental experts. Despite the brief exchange, the overall tone of the evening was forward-looking. Residents lingered after the formal discussion to review informational materials, speak with industry representatives, and learn about opportunities for community involvement. For many, the message was clear: Maryland’s transition to clean energy is not only feasible, it’s already underway, and the Eastern Shore stands to benefit.