Sheep and Solar Panels: Using Solar Sites for Pastureland

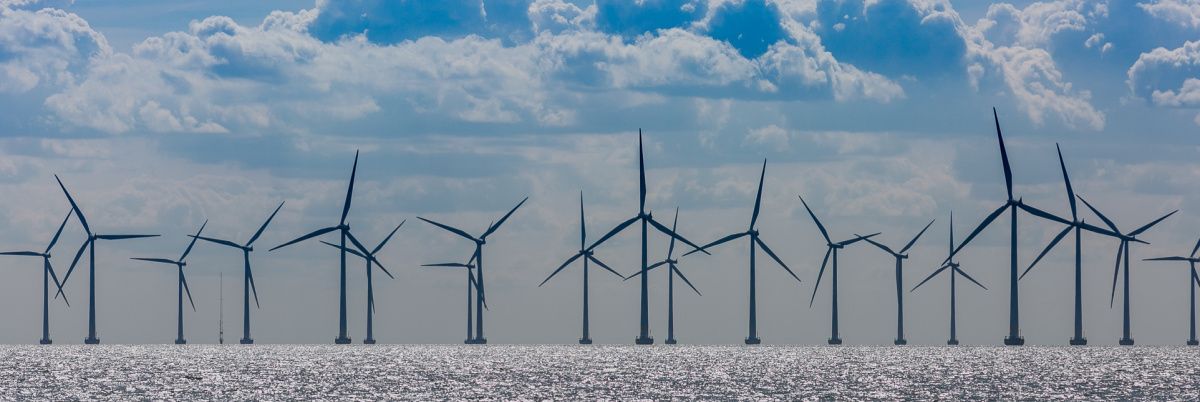
A solar power boom generated by new renewable energy mandates is unfurling in the Chesapeake Bay region. Virginia, for example, was ninth in the nation for new solar capacity in 2021.
With many solar arrays ending up on farmland, a movement is fast taking hold to make sure that they will benefit the environment, agriculture and wildlife, and not just create a sea of silicon.
Allowing sheep to graze among solar panels has become one attractive antidote.
Grazing by sheep and other livestock joins other dual uses: planting groundcover to benefit pollinators, growing marketable plants such as cherry tomatoes and lavender under the panels, installing beehives and maximizing soil health practices to improve the land for later ag use. Projects that combine farming and solar energy are called agrivoltaic.
State agencies in Virginia, Maryland, and New York have all created pollinator-friendly scorecards for solar developers, underscoring the expectation that environmentally beneficial groundcover will become the norm on both rural and urban solar farms.
“Solar [arrays] on farmland should be required to be dual use,” said Arjun Makhijani, founder of the Maryland-based Institute for Energy and Environmental Research.
The use of solar sites for livestock grazing is still in its infancy, but flocks of sheep are already grazing contentedly under and around glass panels in Pennsylvania, Virginia, Maryland, and New York.
By welcoming the grazers, solar operators save money on land maintenance. After the cost of leasing the land, vegetation management is often their top expense.
Sheep owners get access to new grazing pastures while receiving payments to boot, adding precious income at a time when many farmers are struggling. Studies find that sheep farmers often are paid $300–$500 an acre.
There are environmental benefits as well. For example, a new study funded by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that native vegetation munched on by sheep shows an uptick in carbon capture and improves the soil by increasing the cycling of nutrients, carbon and water.
The synergies of grazing and leaving the ground undisturbed can actually improve a farm’s soil during its use as a solar site, according to a study by the Institute for Energy and Environmental Research, based on solar projects on three Maryland farms. Farmers want and financially need the opportunity, the study said.
Why are sheep the most popular choice, at least for now? Because most solar arrays are too close to the ground to accommodate cattle. A solar project being built in Howard County, Md., though, has panels 6 feet off the ground so cows can graze on hay planted underneath. Goats tend to eat wiring and jump onto the panels. Pigs wallow.
Sheep, on the other hand, fit nicely under the panels, typically built two to three feet off the ground, and they keep their heads down for the business at hand. The panels provide shelter and shade. Studies are also finding that vegetation planted for grazing under solar panels helps keep the panels cool, boosting energy production.
“Normally, we hired crews with lawn mowers and weed wackers. For a solar business focused on sustainability, the idea of using fossil-fuel equipment is counterintuitive,” said Keith Hevenor of Nexamp Inc., one of the largest solar developers in the nation. The New Jersey-based company has sheep grazing at 14 sites in New York and may double that total by the end of the year.
“It’s been a great fit for us,” he said.
And then there are the optics. At some sites, solar grazing has blunted the concerns of those rattled by the conversion of farmland to energy production. Twenty states have sheep grazing on solar sites.
It seems too good to be true. But it’s not, said New York sheep farmer Lexie Hain, who helped form the grassroots American Solar Grazing Association in 2018 to connect and mobilize sheep farmers and solar operators around the country.
“Sheep are the natural fit for solar. It’s creating a shift,” Hain said. “This is a land-use change as well as a business opportunity for people, and they are responding. Solar grazing is happening on its own because it works better than mechanical mowing. It’s kind of remarkable.”
She and her nonprofit are being flooded with requests for advice and have helped launch grazing at solar arrays in Virginia, Pennsylvania, and New York and other states. Hain and a business partner graze 1,400 of their own sheep at eight solar sites in New York and Pennsylvania.
The growing interest has already prompted a seed mix specially designed for solar grazing by sheep. Fuzz & Buzz by Pennsylvania-based Ernst Conservation Seeds combines various nutritious grasses favored by sheep with blooming plants that draw pollinators and improve soil health.
Fat as butterballs
In the spring of 2020, John Fisher and his son, who are Amish sheep farmers near Gettysburg, PA, turned loose 100 lambs inside the newly opened 130-acre Nittany 1 solar array erected by Lightsource BP on former farmland.
“Those lambs gained weight like crazy, more than sheep ever gained on our pastures,” Fisher said.
Things went so well that this past season the brothers have increased the number of sheep they grow for meat on the property to 480. To keep from overgrazing the ground bare, the sheep are rotated into new areas of the property every few days with moveable fences.
The best grazing was under the solar panels themselves, he said. Studies have shown that “microclimates” of heat and moisture develop under panels, providing ideal growing areas for an assortment of vegetables, berries and marketable niche plants such as saffron.
“I couldn’t have found a better pasture for my sheep, in all honesty,” Fisher said when asked if he was satisfied with the grazing arrangement. Coreopsis, goldenrod, ox-eyed daisies, milkweed and other flowering plants added to the mix to benefit bees and other pollinators had “blooms all over the place,” the grazier reported.
About 100 miles east, near Sunbury and the Susquehanna River, grazier Caroline Owens lets 40 sheep she raises for meat, wool and public education fatten up on a 14-acre solar array. The panels there power 30% of the surrounding campus of Susquehanna University. The college initiated the grazing venture with her three years ago. Now, the sheep share the site with a beehive and communal gardens for students.
“They have everything they need. They’re butterball fat,” she said.
Are there enough sheep to do the job?
With the accelerating interest in solar grazing, the question may soon be if there are enough sheep to go around.
On average, it takes about one to five sheep per acre to keep plant growth trimmed.
In Virginia, where an estimated 7,500 to 35,000 acres will be needed for solar projects to meet the state’s goal of 50% renewable energy by 2020, there are 72,000 sheep. Approximately 417 solar projects are awaiting approval from PJM Interconnection, the nation’s largest electric grid operator. At the upper end of the estimated need for solar acres, there would not be enough sheep to cover that ground.
Pennsylvania has about 96,000 sheep, according to the National Agricultural Statistics Service. Under Gov. Tom Wolf’s 2019 executive order to lower greenhouse gas emissions by 80% by 2050, some estimates say 80,000 acres of solar arrays will be needed in the next eight years. Approximately 437 solar projects are awaiting review by PJM Interconnection, a majority on open land. Pennsylvania would have a deficit of sheep unless only one or two sheep are needed to keep grasses shorn.
In Maryland, the state had mandated that 14.5% of its energy come from solar sources by 2030 — triple the amount installed now. That was before the Climate Solutions Now Act became law this spring, speeding up the targeted rate of greenhouse gas reductions. Under the former law, a governor’s task force estimated that 7,766 to 33,033 acres of farmland would be needed to meet the goal. Currently, there are an estimated 23,400 sheep on 925 farms of various sizes. That would not be enough sheep to handle the upper estimate of needed solar acres.
“I think there’s a lot of interest [in solar grazing] in Maryland. I’m not certain we have enough sheep,” said Susan Schoenian, a sheep and goat specialist at the University of Maryland’s Western Maryland Research and Education Center.
New York, which has one of the most ambitious clean-energy goals in the nation, has 80,000 sheep.
Challenges include transportation to distant solar sites and lack of awareness of solar grazing opportunities. That’s why Todd Schmidt is working on a three-year study, funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and Schmidt’s own Cornell University, for ways to increase solar grazing in Pennsylvania, New York and other mid-Atlantic and New England states.
Sheep farmers forming cooperatives that can buy and share transportation — even marketing sheep meat as “produced under solar arrays” — are among the ideas to increase the sheep-solar connection.
“I think from a policy standpoint, there is considerable interest from state legislatures that this needs to be considered,” Schmidt said.
Hain and others said that they believe the demand for solar grazing create growth in the sheep industry. Plus, the relatively low costs of starting a sheep farm is attractive to entry-level participation by young and beginning farmers, as well as people of color.
“Sheep farming in the United States hasn’t really taken off because it hasn’t been a profitable venture,” said Caleb Scott, a New York sheep farmer and vice president of the American Solar Grazing Association. “But now, with the opportunity to provide a service through feeding your sheep, it’s increasingly making sheep farming maybe one of the most profitable animal husbandry markets that’s scalable.”
A workable tradeoff?
Despite its multiple benefits, sheep grazing among solar fields has not been universally embraced and is seen by some as enabling the conversion of prime farmland to energy production. Some think solar belongs only or primarily on rooftops, parking lots, abandoned mine land and industrial or commercial sites.
Especially where prime soil is taken out of production, some groups don’t want to see farmland converted into industrial energy sites, even if theoretically the land can resume agricultural use, on healthier soil, after solar contracts end, typically in 25 years.
Roughly 61% of solar arrays built on Virginia farmland so far have been on the highest-rated soil, according to a study by Aaron Berryhill of Virginia Commonwealth University.
“The scale and pace at which this is happening means reasonable mitigation measures need to be strengthened,” said Ethan Winter, the American Farmland Trust’s northeast solar specialist.
While solidly endorsing solar energy, the Chesapeake Bay Foundation says solar arrays should avoid prime farmland and the removal of trees. A planned 7-acre community solar project on the foundation’s Clagett Farm in Maryland will incorporate an existing herd of sheep for vegetation management and to increase the herd size.
Grazing may not address all concerns, but it is playing a role in handling the increasing pressure for multiple benefits from solar sites.
“It doesn’t necessarily solve the problem of prime farmland going into solar developments and loss of farmland,” Schmidt said. “But maybe it’s a middle-ground strategy.”
Ad Crable is a Bay Journal staff writer based in Pennsylvania.
This article was originally published in the Bay Journal, a non-profit news source that provides the public with independent reporting on environmental news and issues in the Chesapeake Bay watershed.
Common Sense for the Eastern Shore